Question
Question: A heat engine undergoes a process in which its internal energy decreases by \(400\,J\) and it gives ...
A heat engine undergoes a process in which its internal energy decreases by 400J and it gives out 150J of heat. During the process
A. It does 250 J of work and its temperature rises
B. It does 250 J of work and its temperature falls
C. It does 550 J of work and its temperature rises
D. It does 550 J of work and its temperature falls
Solution
A heat engine is a device that converts heat energy into mechanical energy. It does this by undergoing some certain process in which it takes heat energy from a heat source and then converts some of the heat energy into useful work and releases the rest heat energy to the heat sink.
Complete step by step answer:
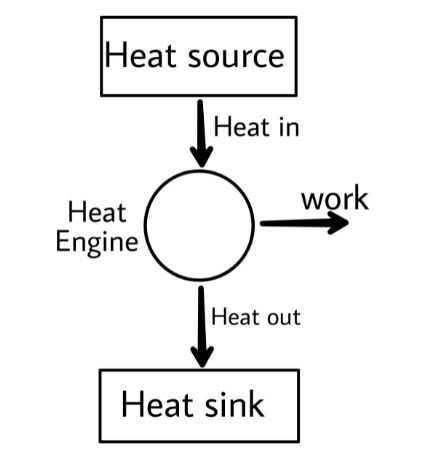
In the above diagram the engine takes heat energy from a heat source and then converts some of the heat into useful work and releases the rest to the heat sink. Now by the basic concept of thermodynamics we know that the internal energy of the system is a function of temperature only (directly proportional to the temperature of the system) and it does not alter itself unless the temperature is altered.
In this question the internal energy of the system decreases which means that the temperature also falls down to some extent. Now the engine’s internal energy is decreased by a factor of 400J and it releases 150J (to the heat sink) which means the rest of the missing energy is utilized as useful work.
Work done 400J−150J=250J
Work done =250J
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Heat engines mostly work on this principle giving part of heat as useful work and the rest to the heat sink, here we have ignored any kind of energy loss due to friction. If the friction force is taken into encounter, then the heat taken from the heat source is divided into three parts, one part used to get useful work, the other part is released to the heat sink and the last part is dissipated as energy loss due to friction.
