Question
Question: A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixe...
A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in the Fig.2.4. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it? Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.
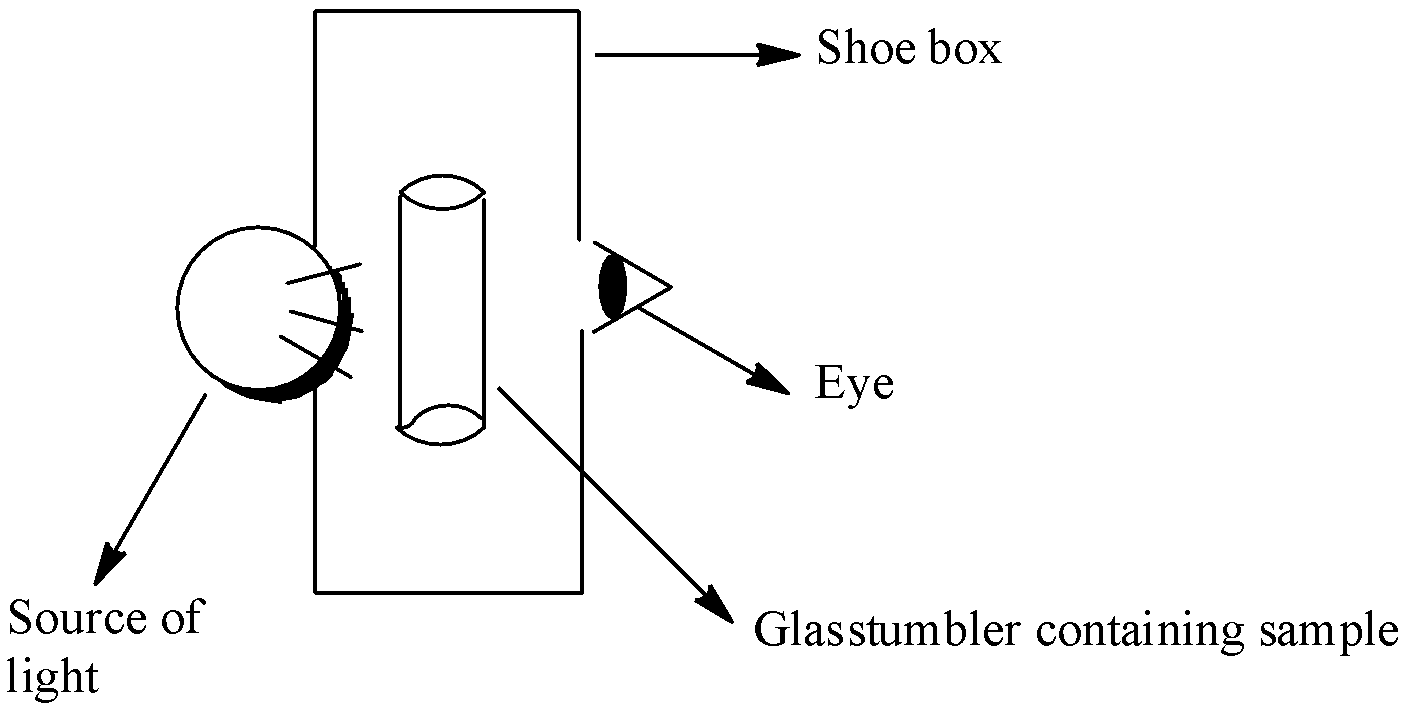
Fig. 2.4
Solution
If the size of the particles of the milk is in the range of the size between 1 nanometer to 1000 nanometer then these particles will cause the scattering of light which is a specific phenomenon caused by the particles only of this range.
Complete answer:
The students took two samples in this experiment that is milk and saltwater. We know that the salt solution is a homogenous solution that means the salt is completely soluble in water forming a true solution.
The size range of particles of the milk is in the range between the 1 nanometer to 1000 nanometer, which is the size range of colloidal particles. But the size range of the particles of the salt solution is in the range of less than 1 nanometer which is the size of true particles.
Hence the milk is a colloid and the salt solution is a true solution.
There is the illumination of light due to the Tyndall effect of the colloidal particles. The Tyndall effect is an optical effect, which may be defined by the scattering of the light by the particles. The true solutions do not give a Tyndall effect due to which there is no illumination of light.
Hence the phenomenon is due to the Tyndall effect of the colloidal particles.
Note:
There are other properties like the Brownian effect in which the colloidal particles move in the zig-zag pattern, coagulation in which the colloidal particles come together and form large particles, etc.
