Question
Question: A girl standing at point P on a beach wishes to reach a point Q in the sea as quickly as possible. S...
A girl standing at point P on a beach wishes to reach a point Q in the sea as quickly as possible. She runs at 6km/hr on the beach and swims at 4km/hr in the sea. She should take the path
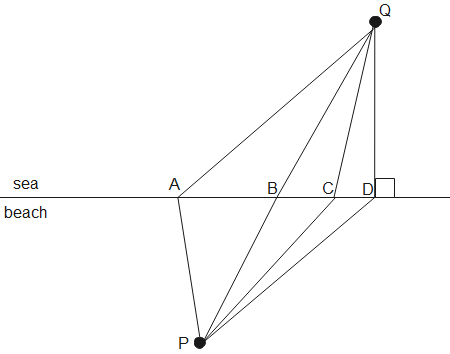
(A). PAQ
(B). PBQ
(C). PCQ
(D). PDQ
Solution
In optics, Snell’s law is defined as the relationship between the path taken by the ray of light while crossing the boundary or the surface of separation between the two contacting substances and the refractive index of each.
Complete step by step solution:
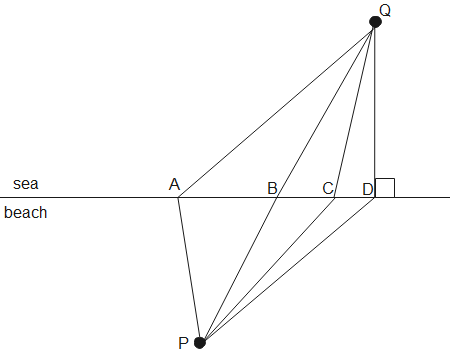
When light travels from one medium to the other it changes its path, this phenomenon is known as refraction.
So whenever light goes from one medium to the other, it tends to take the smallest path, through which minimum time will be covered. This is the fact which led to the derivation of Snell’s law.
Snell’s law states that the refractive index is the ratio of velocity of light in air to the velocity of light in medium.
When refraction occurs, the light bends towards the normal in denser medium but bends away from the normal in rarer medium. At the beach the velocity of a girl is greater but will decrease as it goes into the sea. So the path at the sea should be more towards the normal.
In the figure, the path PCQ should take the least time to travel between points P and Q.
Therefore, the shortest path is PCQ, hence the correct option is (C).
Note: Snell's law in terms of angles is the ratio of angle of incidence to the angel of refraction. When light travels from rarer to denser medium, after a certain limiting angle, called the critical angle total internal reflection occurs. The speed of light is slower in denser mediums and faster in rarer mediums.
