Question
Question: A galvanometer of resistance \(25ohm\) is connected to a battery of \(2V\) along with a resistance i...
A galvanometer of resistance 25ohm is connected to a battery of 2V along with a resistance in series. When the value of this resistance is 3000, a full scale deflection of 30 units is obtained in the galvanometer. In order to reduce this deflection to 20 units. The resistance in series will be
Solution
Hint When calculating the current passing through the galvanometer, we have to consider the resistance of the galvanometer as well as the resistor connected in series. The higher the resistance in series, the lower the current through the galvanometer.
Formula Used:
We have used only Ohm’s law in this problem. It is given by
V=IR
Where V is the voltage applied.
I is the current through the resistor.
R is resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
We can visualize the circuit given in this problem as follows
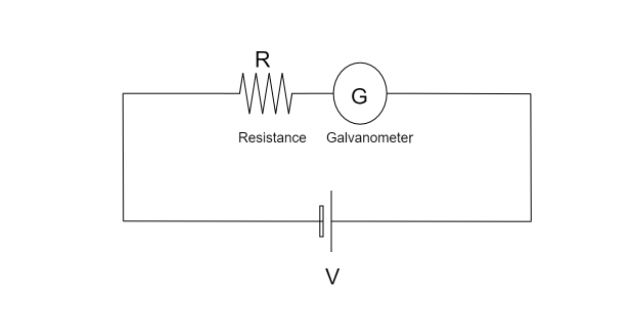
According to Ohm’s law, we know that
V=IR
This formula can be modified for this problem as
V=Ig(R+G)
⇒Ig=(R+G)V −−−−(1)
Where G is the resistance offered by the galvanometer which is given as G=25Ω.
We have connected a battery of potential V=2V to the galvanometer and resistor of resistance, R=3000Ω.
Ig=(3000+25)2 −−−−(2)
We know that Galvanometers are used to detect current and it is given that a full-scale deflection of 30 units is observed.
So, we can write that
Ig=30×g −−−−(3)
⇒g=30Ig −−−−(4)
Where g is the figure of merit of the galvanometer.
Using equation (2) and (4), we get the value of the figure of merit as
g=(3000+25)×302 −−−−(5)
Initially, for R=3000Ω deflection was 30 units in the galvanometer.
Now, we need a deflection of 20 units in the galvanometer.
Similarly, it can be written that the required current is
Ig=20×g −−−−(6)
Using the equation(1), we know that current is given by the formula
Ig=(R′+G)V −−−−(7)
Where R′is the adjusted resistance.
So comparing equations (6) and (7),
20×g=(R′+G)V
(R′+G)=20×gV
Putting V=2Vand the figure of merit (g) from the equation(5), we get
(R′+G)=202×2(3000+25)×30
⇒(R′+G)=4537.5
Using G=25Ω
R′=4512.5Ω
Thus, the resistance that we need to get a deflection of 20 units in the galvanometer is 4512.5Ω.
Note Be very careful with the position of the external resistor. If the resistor is in series we follow this method. If the resistance is in parallel, then you have to derive the appropriate formula for such circuits. If the resistance is in parallel, the higher the resistance value, the more current will pass through the galvanometer.
