Question
Question: A galvanometer coil has a resistance \(90\Omega \) and full-scale deflection current \(10mA\). A \(9...
A galvanometer coil has a resistance 90Ω and full-scale deflection current 10mA. A 910Ω resistance is connected in series with the galvanometer to make a voltmeter. If the least count of the voltmeter is 0.1V, the number of divisions on its scale is
A. 90
B. 91
C. 100
D. None
Solution
Hint: Design the circuit for the voltmeter and apply the Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the new circuit. For a full deflection current in the galvanometer, find the range of the voltmeter designed. Apply the formula for the number of divisions using the least count and the range to find the answer.
Formula used: Ohm’s law:
V=iR
Formula for number of divisions:
Number of divisions=least countRange of the device
Complete step-by-step answer:
A galvanometer is an instrument which is used to measure the current flowing in a circuit and it is added to the circuit in series. The figure shows the circuit of a galvanometer.
To the galvanometer of resistance Rg=90Ω an additional resistance of R=910Ω is added to the circuit to use it as a voltmeter. A voltmeter is a device used to measure voltage across two points in a circuit and it is added in parallel to the circuit.
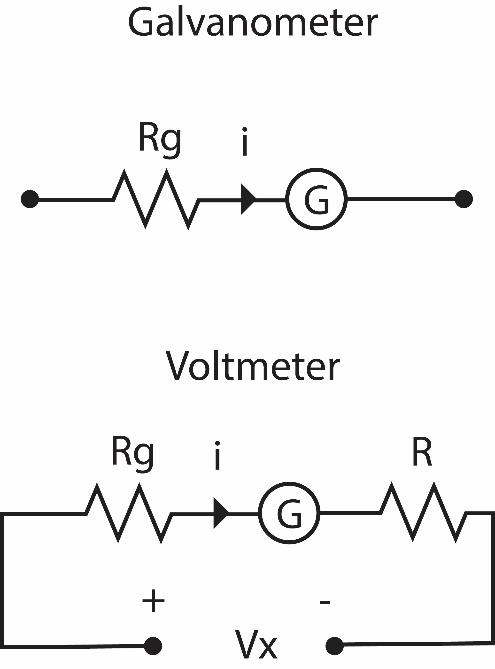
The voltmeter and the galvanometer work on the principle of Ohm’s law. Which gives us the formula:
V=iR
The following figure shows the circuit for the voltmeter we built. It measures the voltage across the ends A and B. Applying KVL (Kirchhoff’s voltage law) in the circuit, we get the expression:
Vx=i(R+Rg)=1000i
Here i is the current that the galvanometer measures. Since, the galvanometer can only show a deflection up to 10mA, the maximum that our voltmeter can show will be 1000×10×10−3V=10V.
Since the least count of the voltmeter is 0.1V, the number of divisions can be given by the formula:
Number of divisions=least countRange of the device⇒Number of divisions=0.1V10V=100
Therefore, the correct answer is option C. 100.
Note: Students can get confused how to design the circuit for the galvanometer and the voltmeter. Note that galvanometer is added to the circuit in series with small value of resistance to ensure the original value of the voltage difference in the circuit varies negligibly. Similarly, voltmeter is added in parallel to the circuit. The resistance in the voltmeter is high to ensure only a small current passes through the voltmeter branch, varying the original current in the circuit negligibly.
