Question
Question: A flat plate is moving normal to its plane through a gas molecule under the action of a constant for...
A flat plate is moving normal to its plane through a gas molecule under the action of a constant force F. The gas is kept at a very low pressure. The speed of the plate v is much less than the average speed u of the gas molecules. Which of the following options is / are true?
(A) The resistive force experienced by the plate is proportional to v
(B) At a later time external force F balances the resistive force
(C) The plate will continue to move with constant non zero acceleration, at all times
(D) The pressure difference between the leading and trailing faces of the plate is proportional to uv .
Solution
The plate and the gas molecules which surround it undergo the collision when it moves from one place to the other by the external force. The gas molecules may be resistant to the movement of the plate.
Formula used:
The momentum is given by
M=m(v+v0)2nAdt
Where M is the momentum of the plate and the surrounding gas molecules, m is the mass of the plate, v0 is the initial velocity and the v is the final velocity of the molecules and A is the area of the plate.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
The speed of the plate is v
The speed of the gas molecules is u
u>v
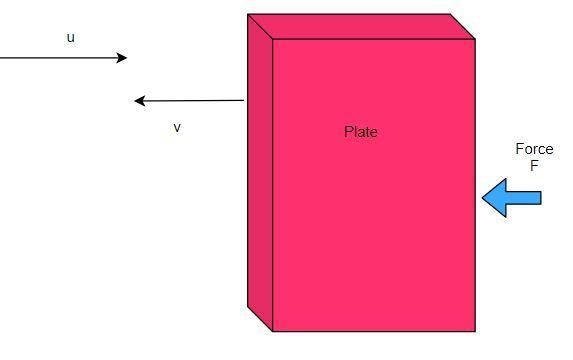
Let us assume that the number of gas molecules is n. When the plate is moved by some external force, the gas molecules also move along with it.
Hence the relative speed of the molecules is given by u+v.
Hence the resistive force of the air also depends on the speed of the plate. Thus option (A) is correct.
Using the formula of the momentum,
M=m(v+v0)2nAdt
The momentum is transferred from the front surface to the back surface is m(u+v)2nAdt and m(u−v)2nAdt
Respectively.
Hence the net force is calculated by
F=m(u+v)2nAdt+m(u−v)2nAdt
By simplifying the above equation,
F=mnA(4uv)
F∝uv
Hence the net force balances the resistive force. Hence the option (B) is also correct.
The pressure difference is given by subtracting the leading pressure and the trailing pressure.
dP=mn(v+u)2−mn(u−v)2
By simplifying the above equation,
dP=4mnuv
dP∝uv
Hence the option (A), (B) and (D) are correct.
Note: It is to be remembered that the law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum before and after collision remains the same. The speed of the gas molecules surrounding the plate determines the force, momentum and the pressure difference.
