Question
Question: a. Draw the geometrical isomer of complex \(\left[ {{\text{Pt}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\tex...
a. Draw the geometrical isomer of complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2].
b. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δ0<P.
c. Write the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Ni(CO)4]. (At. no. of Ni=28).
Solution
The complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is a [Ma2b2] type of complex. Δ0 is the crystal field splitting energy and P is the pairing energy. When Δ0<P, it is a weak field ligand. The outer electronic configuration of nickel is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d8.
Complete step by step solution:
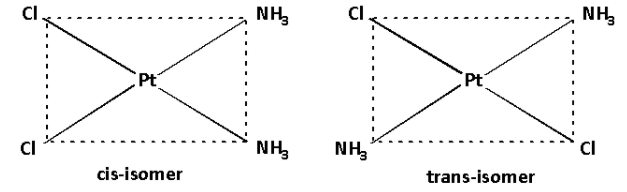
a. The complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] is a [Ma2b2] type of complex. These kind of complexes have two types of geometrical isomers.
The cis isomer is obtained when the same ligands are adjacent to each other.
The trans isomer is obtained when the same ligands are opposite to each other.
Thus, the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] are as follows:
b. When the ligand bonds to the metal ion, the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases. As the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases, the degenerate orbitals split into t2g and eg orbitals.
The difference in the energies of the t2g and eg orbitals is known as the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). It is denoted by Δ0.
When Δ0<P i.e. crystal field splitting energy is smaller than the pairing energy, the ligand is a weak field ligand. When the ligand is a weak field ligand, the fourth electron jumps in the eg orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration for d4 ion is as follows:
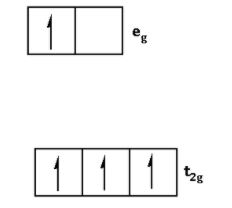
Thus, on the basis of crystal field theory, the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δ0<P is t2g3eg1.
c. The electronic configuration of nickel is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d8.
The outer electronic configuration is 3d84s24p0.
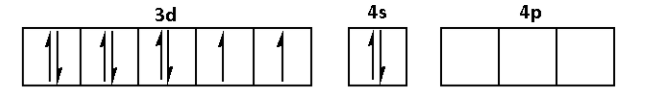
In the complex [Ni(CO)4], CO is a strong ligand. Thus, it will cause the pairing of electrons.
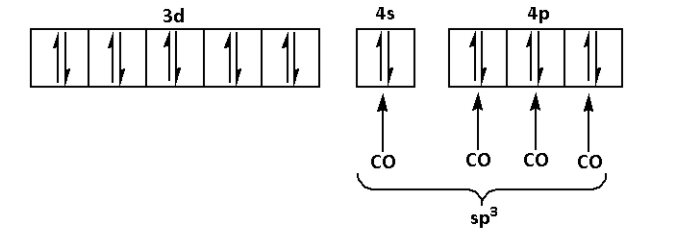
Thus, the hybridisation of the complex [Ni(CO)4] is sp3.
The complex [Ni(CO)4] does not have any unpaired electron. Thus, the complex [Ni(CO)4] is a diamagnetic complex.
Note:
Strong field ligands form low spin complexes. The examples of strong field ligands are CO, CN−. Weak field ligands form high spin complexes. The examples of weak field ligands are F−, Cl−. The complexes having unpaired electrons are paramagnetic in nature and those having no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic in nature.
