Question
Question: a) Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). Write its half-cell reaction of \({{\...
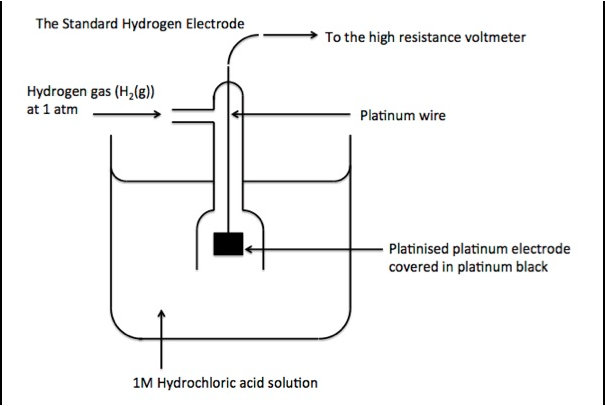
a) Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE). Write its half-cell reaction of E0 value.
b) Calculate ΔrG0 for the following reaction:
Fe+2(aq)+Ag+→Fe+3(aq)+Ag(s), (GivenE(cell)0=+0.03V,F=96500C)
Solution
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode, is a redox electrode which is the basic of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potential. It is basically used as a reference electrode on half-cell potential reactions. The value of the standard electrode potential is zero, which forms the basis to calculate cell potentials using different electrodes or different concentrations.
Complete answer:
The Standard Hydrogen Electrode also known as SHE. The potential of SHE is always 0 at 298K, this is the reason it is used as a reference electrode.
The redox half-cell reaction of the SHE is:
2H+(aq)+2e−→H2(g) E0
Hydrogen Standard electrode potential (E0) is declared as zero at any temperature.
Addition Information:
The absolute electrode potential of SHE is measured to be 4.44+-0.02V at room temperature. But for a basic comparison with all other electrode reactions, Hydrogen standard electrode potential (E0) is declared to be zero volts at any temperature.
The reasons for choice for platinum for the hydrogen electrode is:
-Inertness of platinum
-The capability of platinum to catalyze the reaction of proton reduction
-Use a surface material that absorbs hydrogen well at its interface. This increases the reaction kinetics
Note:
The value of standard electrode potential is always zero. During the reaction, hydrogen gas is passed through and into the solution and the reaction that takes place is: 2H+(aq)+2e−→H2(g)
b) Calculate ΔrG0 for the following reaction:
Fe+2(aq)+Ag+→Fe+3(aq)+Ag(s), (GivenE(cell)0=+0.03V,F=96500C)
