Question
Question: A current of 1 ampere is passed through a straight wire of length \(2.0m\). What will be the magneti...
A current of 1 ampere is passed through a straight wire of length 2.0m. What will be the magnetic field at a point in air at a distance of 0.3m from either end of the wire and lying on the axis of wire ?
(A) 2πμ0
(B) 4πμ0
(C) 8πμ0
(D) zero
Solution
In order to solve this problem first draw a diagram in which point P is shown perfectly with wire.
After that use the formula of the magnetic field due to wire derived with the help of Biot – Savart law which is :
dB=4πμ0r3I(dℓ×r)
Now put the angle between dℓ and r zero because the P point is situated at the axis of the wire.
Finally we get a magnetic field at point P.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the magnetic field due to wire is given as
dB=4πμ0r3I(dℓ×r) …..(1)
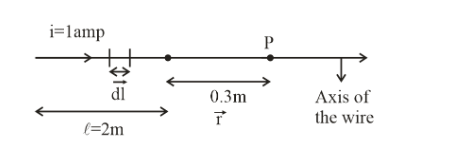
Here direction of dℓ and r is same i.e., angle between then is zero, so, the cross product of them is zero i.e., dℓ×r=∣dℓ∣∣r∣sinθ
=∣dℓ∣∣r∣sin0
dℓ×r=0 …..(2)
So, from equation 1 & 2, we get
dB=0
∴B=0
Hence, the magnetic field at point P i.e., at the axis of the wire is zero.
So, option D is the correct answer zero.
Note: Here students may get confused between methods of calculating magnetic fields due to wire.
There are 2 laws :
(1) Biot – Savart law
(2) Ampere’s Circuital law
-The second point at which student may get confused is that where the point is situated i.e.
-If point is situated at the axial line then magnetic field B=0 because θ=0∘
-If point is not at the axis of wire then magnetic field due to wire at any point is given as
BP=2πrμ0I because θ=90∘