Question
Question: A covalent molecule M contains a total of four shared electrons. What is M? A.Ammonia B.Hydrogen...
A covalent molecule M contains a total of four shared electrons. What is M?
A.Ammonia
B.Hydrogen chloride
C.Methane
D.Water
Solution
A chemical reaction involving the exchange of electron pairs between atoms is known as a covalent bond. Shared pairs or bonding pairs are the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons, and covalent bonding is the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons.
Complete answer:
Elements with very high ionisation energies are unable to pass electrons, while those with extremely low electron affinity are unable to absorb electrons. These elements' atoms appear to exchange electrons with atoms of other elements or with atoms of the same element in such a way that all atoms maintain an octet structure in their respective valence shells and hence achieve stability. The term "covalent bond" refers to a connection formed by the exchange of electron pairs among different or similar kinds of molecules.
Carbon, according to its electronic structure, has to gain or lose four electrons to become stable, which is unlikely because: Carbon cannot gain four electrons to become C4−because six protons would struggle to carry ten electrons, causing the atom to become unstable.
Carbon cannot lose four electrons to become C4+ because doing so would take a lot of energy, and C4+ would only have two electrons retained by the proton, making it unstable once again.
Since carbon cannot receive or donate electrons, it must exchange an electron to complete its closest noble gas configuration and form a covalent bond.
Hence Methane will be the correct answer. It consists of 4 shared electrons with Hydrogen.
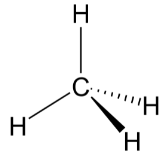
Methane, with the molecular formula CH4, is the most basic of the saturated hydrocarbons. The simplest alkane is made up of four hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom.
Atmospheric methane is formed as natural methane meets the surface of the earth, and it can be present both beneath the seafloor and underneath the crust.
Note:
Methane has no colour and is odourless or has a sweet oily scent. It's a non-toxic, flammable gas. It's a tetrahedral molecule with four C-H bonds that are identical. Anaerobes in the colon contain it. In the year 1776, Alessandro Volta, an Italian astronomer, was the first to scientifically recognise methane.
