Question
Question: A coordination complex of type \(M{{X}_{2}}{{Y}_{2}}\) (M – metal ion; X,Y – monodentate ligands), c...
A coordination complex of type MX2Y2 (M – metal ion; X,Y – monodentate ligands), can have either a tetrahedral or a square planar geometry. The maximum number of possible isomers in these two cases are respectively.
A. 1 and 2
B. 2 and 1
C. 1 and 3
D. 3 and 2
Solution
A monodentate ligand, in a complex is attached with the central metal ion, only through one donor site. While a polydentate ligand is attached from more than two donor sites.
Complete step by step solution: Stereo isomerism in chemical complexes leads to various shapes of the complexes. The type MX2Y2complex can either have tetrahedral or square planar geometry.
In tetrahedral geometry, the ligands are attached adjacent to the central metal ion, which does not lead to any type of isomerization, so isomer structure is only 1 in this case. The shape is as follows:
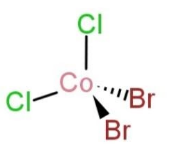
While in square planar shape of a complex with the type MX2Y2, the isomers are cis, and trans. In cis, the groups are at adjacent sides, while in trans, the groups are on opposite sides. So, two isomers exist in this type with square planar. The isomers are:
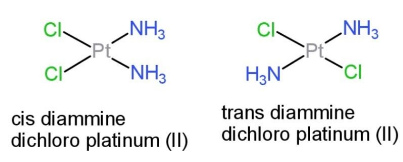
Hence, maximum isomers in tetrahedral geometry can be 1 and that in square planar 2.
Additional information: cis diammine dichloro platinum (II) is also known as cisplatin, which is used in the treatment of cancer.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Some examples of monodentate ligands are, NH3,H2O,Cl−,Br−,CN−, all halogens are monodentate. While polydentate ligands are, oxalate and EDTA.
