Question
Question: (a) Complete the following chemical equations: (i) \({\text{NaOH (hot and conc}}{\text{.)}} + {\te...
(a) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) NaOH (hot and conc.)+Cl2→
(ii) XeF4+O2F2→
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) H3PO2
(ii) H2S2O7
(iii) XeOF4
Solution
Draw the structures of the molecules by counting the valence electrons for the molecule. The valence electrons are donated by dots around the atoms and are called electron dot structures.
Complete step by step answer:
(a)(i) Complete the chemical equation NaOH (hot and conc.)+Cl2→:
Hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride, sodium chlorate and water.
The chemical formula for sodium chloride is NaCl and the chemical formula for sodium chlorate is NaClO3.
Thus, the chemical equation is as follows:
NaOH (hot and conc.)+Cl2→NaCl+NaClO3+H2O
The balanced chemical equation is as follows:
6NaOH (hot and conc.)+3Cl2→5NaCl+NaClO3+3H2O
(ii) Complete the chemical equation XeF4+O2F2→:
Xenon tetrafluoride reacts with fluorine dioxide to form xenon hexafluoride and oxygen gas.
The chemical formula for xenon hexafluoride is XeF6.
Thus, the chemical equation is as follows:
XeF4+O2F2→XeF6+O2
(b)(ii) Draw the structures of H3PO2:
Calculate the valence electrons of H3PO2 molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of hydrogen are one, phosphorous are five and oxygen are six. Thus,
Valence electrons of H3PO2
=(3×Valence electrons of H)+(1×Valence electrons of P)+(2×Valence electrons of O)
=(3×1)+(1×5)+(2×6)
= 3 + 5 + 12
Valence electrons of H3PO2 =20
Draw the Lewis structure of H3PO2 as follows:
The structure of H3PO2 is,
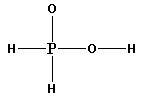
As five bonds are formed, ten electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 20 - 10 = 10
Place the remaining 10 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of H3PO2 is as follows:
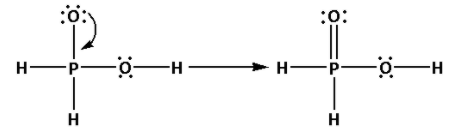
(ii) Draw the structures of H2S2O7:
Calculate the valence electrons of H2S2O7 molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of hydrogen are one, sulphur are six and oxygen are six. Thus,
Valence electrons of H2S2O7
=(2×Valence electrons of H)+(2×Valence electrons of S)+(7×Valence electrons of O)
=(2×1)+(2×6)+(7×6)
= 2 + 12 + 42
Valence electrons of H2S2O7 =56
Draw the Lewis structure of H2S2O7 as follows:
The structure of H2S2O7 is,
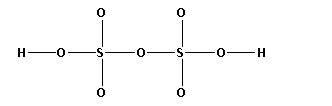
As ten bonds are formed, twenty electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 56 - 20 = 36
Place the remaining 36 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of H2S2O7 is as follows:
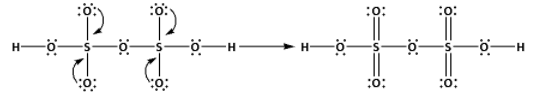
(iii) Draw the structures of XeOF4:
Calculate the valence electrons of XeOF4 molecule as follows:
The valence electrons of xenon are eight, oxygen are six and fluorine are seven. Thus,
Valence electrons of XeOF4
=(1×Valence electrons of Xe)+(1×Valence electrons of O)+(4×Valence electrons of F)
=(1×8)+(1×6)+(4×7)
= 8 + 6 + 28
Valence electrons of XeOF4 =42
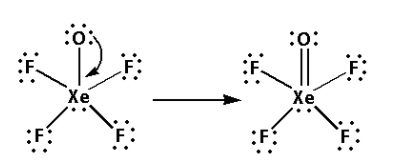
Draw the Lewis structure of XeOF4 as follows:
The structure of XeOF4 is,
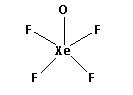
As five bonds are formed, ten electrons are involved in bonding. Thus, the remaining electrons are,
Remaining electrons = 42 - 10 = 32
Place the remaining 32 electrons around the oxygen atoms such that all the oxygen atoms complete their octets.
Thus, the structure of XeOF4 is as follows:
Note: Steps to determine the structure of a molecule are as follows:
- Determine the number of total valence electrons. (The number of valence electrons of an atom is equal to the number of the group in which the atom lies.)
- Determine the number of electrons involved in bonding.
- Determine the number of remaining electrons.
- Draw the Lewis structure.
