Question
Question: A closed tank has two compartments A and B, both filled with oxygen (assumed to be an ideal gas). Th...
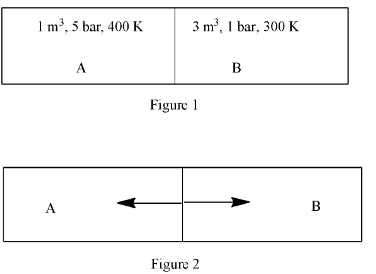
A closed tank has two compartments A and B, both filled with oxygen (assumed to be an ideal gas). The partition separating the two compartments is fixed and is a perfect heat insulator (Figure 1). If the old partition is replaced by a new partition, which can slide and conduct heat does not allow the gas to leak across (Figure 2), the volume (in m3) of the compartment A after the system attains equilibrium is ______________
Solution
We can solve this question by using many formulas like n=TRPV, TAPA=TBPB, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature, n is the number of moles.
Complete step-by-step answer: So according to Figure 1, in compartment A, the pressure is 5 bar, the volume is 1 m3, and temperature 400 K. This can be written as:
PA=5
VA=1
T1=400
In compartment B, the pressure is 1 bar, the volume is 3 m3, and temperature 400 K. This can be written as:
PB=1
VB=3
TB=300
So, from the given values we can calculate the number of moles for both the compartments by using the formula n=TRPV, we get
nA=400 x R 5 x 1=400R5
nB=300 x R 1 x 3=300R3
The total volume will be = 1 + 3 = 4 m3
In Figure 2, let us assume, the volume of A is x and volume of B is (4 – x).
We know that:
TAPA=TBPB, because it will attain equilibrium.
This can be written as:
VA(new)nA x R=VB(new)nB x R
Putting, the values in this, we get:
400(x)5=300(x−4)3
For solving x, we get:
5(4−x)=4x
VA=x=920=2.22
The volume of A after equilibrium will be 2.22 m3.
Note: The formulas that we have used in the question, n=TRPV, and TAPA=TBPB can only be used because the condition was mentioned that the system is an ideal system, if the system is real then we cannot use these formulas.
