Question
Question: A charged rod is brought near a negatively charged pith ball electroscope. What conclusion would you...
A charged rod is brought near a negatively charged pith ball electroscope. What conclusion would you draw about the charge on the rod if the pitch ball moves towards the rod?
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. No charge
D. Can’t say
Solution
A charged pith ball electroscope is a device which is used to check the polarity of charges. It works on the principle that all like charges will repel each other while all opposite types of charges will try to attract each other.
Complete answer:
Electric charge of a material or particle can be defined as a fundamental property of that material or particle by virtue of which it experiences a certain force when it is placed in an electromagnetic field.
There exist two types of charges in nature namely the positive charge and the negative charge. We can differentiate between these charges based on the fact that how they interact with each other when brought in close vicinity of each other.
Pith ball electroscope is a device which was used to understand these charges when they were first discovered. In this electroscope, we have a pith ball which is negatively charged. It is suspended freely and then we bring other charged bodies in the close vicinity of the negatively charged pith ball. It is observed that certain charges attracted the bath while others repelled the ball.
Like charges tend to repel each other while the opposite charges tend to attract each other.
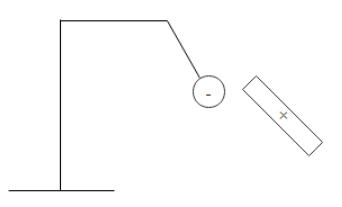
We are given a charged rod which is brought near a negatively charged pith ball electroscope. Now if the pith ball moves towards the rod that means that the two charges are attracting each other and we know that opposite charges attract each other. Since the pitch ball is negatively charged, it means that the rod is positively charged.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
It should be noted that in case if there is no attraction or repulsion when the rod is brought near the pith ball then it means that the rod is uncharged or neutral. In this case, the rod contains equal amounts of positive and negative charge which cancel each other.
