Question
Question: A charged ball B hangs from a silk thread S which makes an angle \(\theta \) with a large charged co...
A charged ball B hangs from a silk thread S which makes an angle θ with a large charged conducting sheet P as shown in the given figure. The surface charge density of the sheet is proportional to:
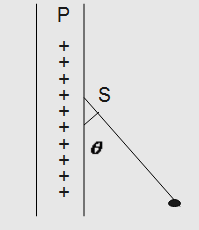
Solution
In this question, we will use the basic expression for Newtonian force experience by an object. Now, by using basic trigonometry we will solve the expression and get the required answer. Further, we will see about the Newtonian force and also, we will see the forces acting on a free body, for better understanding.
Formula used:
F=ma
F=qE
Complete step by step solution:
As, we know the force experienced by the thread in both horizontal and vertical component is given by:
\eqalign{
& T\cos \theta = mg............(1) \cr
& T\sin \theta = qE = q\dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}........(2) \cr}
Now, we divide equation (2) by equation (1):
tanθ=mgε0qσi
∴σ∝tanθ
Therefore, we get the required result.
Additional information:
As we know that when we apply force F on any object, the object experiences other forces as well. These forces balance each other, as shown in the following figure:
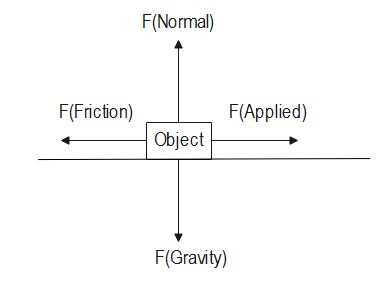
Force is simply any push or pull. We already know that the S.I unit of force is Newton, which is represented by N. Also, we know that the acceleration is defined as the increase in the velocity of an object. The acceleration is measured in meters per Second Square.
There are three laws of motions which are given by the physicist Newton. These three laws of motion relate an object's motion with the forces acting on the object.
Here, the first law of motion states that an object continues to be in rest or in motion in a particular direction until and unless any external force is applied on the object.
Further, according to the second law of motion, the force on an object is equal to its mass times the acceleration. Also, this law also gives us the relation between momentum and force.
Also, the third law of motion states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Note:
We should remember that, Newtonian force and electrostatic force are different, as Newtonian force is force experienced by classical objects and electrostatic force is force experienced by static charges having some distance between them.
