Question
Question: A certain substance A tetramerizes in water to the extent of \(80\% \). A solution of \(2.5g\) of A ...
A certain substance A tetramerizes in water to the extent of 80%. A solution of 2.5g of A in 100g of water lowers the freezing point by 0.3oC. The molar mass of A is:
A. 122
B. 31
C. 244
D. 62
Solution
In this question, we have to take into account the concept of Van't Hoff Factor as the substance undergoes tetramerization in the question because the extent to which a substance associates or dissociates is described only by Van't Hoff factor.
Complete step by step answer: In this question, the concept of depression of freezing point is used. The freezing point of a substance is defined as the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the substance in its liquid phase is equal to the vapour pressure in solid phase. This means that a solution will freeze when its vapour pressure becomes equals to the vapour pressure of pure solid solvent. According to Raoult’s law, when a non-volatile solute is added to the solvent, its vapour pressure decreases and now it would become equal to that of solid solvent at lower temperature. Thus, the freezing point of the solvent decreases.
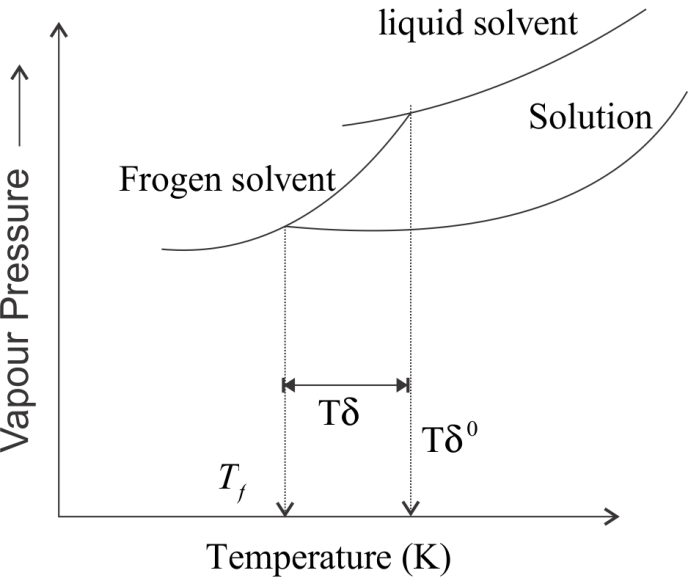
Let Tfo be the freezing point of pure solvent and Tf be its freezing point when non-volatile solute is dissolved in it. The decrease in freezing point i.e. ΔTf=Tfo−Tf is known as depression of freezing point.
Depression of freezing point (ΔTf) for dilute solution is directly proportional to molality m of the solution.
i.e. ΔTf∝m or ΔTf=Kf⋅m
Kf is a constant known as the molal constant of cryoscopic constant.
Now, according to the question, a substance tetramerizes in water i.e. in this question we have to take the concept of Van't Hoff Factor (i). Van't Hoff Factor gives the extent of dissociation or association of a substance. Since the substance tetramerizes (association), so the value of i can be calculated as i=1−∝+n∝ ….. (i)
Here, n becomes 4. Since the extent of association is 80%, means that value of ∝ becomes 80% of 1=0.8. Thus putting all values in equation (i) , we get
i=1−0.8+40.8=0.2+0.2=0.4
i=0.4
Now, the value of depression of freezing point (ΔTf) is 0.3oC and value of Kf as we know for water is 1.86Kg K mol−1.
Now, putting all the values in equation: ΔTf=i⋅Kf⋅m
We get, 0.3=0.4×1.86×m ……………. (ii)
As we know molality is no. of moles of substance present per kg of solvent and is calculate by using m=molar mass of substancegiven mass of substance×weight of solvent(g)1000
Now, the mass of the substance given is 2.5g and the weight of solvent is 100g. Thus molality becomes m=molar mass of substance2.5g×1001000 ……………… (iii)
Now, putting equation (iii) in equation (ii), we get
⇒ 0.3=0.4×1.86×molar mass of solvent2.5×1001000
Or, molar mass of substance =0.3×1000.4×1.86×2.5×1000=62g
Hence, the molar mass of the substance is 62g
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Since the association or dissociation completely is represented by 1. So the 80% association is represented by 80% of 1=0.80. Moreover, the depression in freezing point is used in melting of ice on roads by using NaCl. It is also used as a concept of antifreeze solution.
