Question
Question: A certain alkene produces the product shown, when subjected to ozonolysis followed by oxidative work...
A certain alkene produces the product shown, when subjected to ozonolysis followed by oxidative work-up. What is the structure of alkene?
AlkeneO3H2O2HOOCCH2CH2COOH+CH3COCH3+HCOOH
(A) 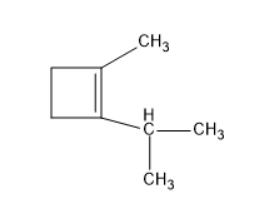
(B) (CH3)2C=CHCH2CH2CH=CH2
(C) CH3CH=CHCH2CH2CH=CHCH2
(D) CH3CH2CH=C=CHCH2CH=CH2
Solution
Alkenes consist of double bonded carbon and carbon atoms. When alkenes are subjected to ozonolysis carbonyl compounds will be formed at the double bond positions. Further oxidative work up converts aldehydes into carboxylic compounds, whereas ketones will remain like that.
Complete answer:
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons consisting of carbon and hydrogen atoms. There will be one or more double bonded carbon atoms in alkenes. When alkenes are subjected to ozonolysis the double bonds will convert into carbonyl compounds which are aldehydes and ketones.
At the position of double bond, the carbonyl compounds will be formed. Aldehydes will convert into carboxylic acid when ozonolysis is followed by oxidation.
In the given option acetone is formed. Thus, the alkenes should consist of an isopropyl group. In the given options, option B has the isopropyl group.
At the position of double bond, the carbonyl compounds will be formed upon ozonolysis.
(CH3)2C=CHCH2CH2CH=CH2O3CH3COCH3+OHCCH2CH2CHO+HCHO
The above products were formed upon ozonolysis and oxidative work up of the above products the aldehydes convert into carboxylic acids.
The oxidative work up the reagent is hydrogen peroxide.
CH3COCH3+OHCCH2CH2CHO+HCHOH2O2CH3COCH3+HOOCCH2CH2COOH+HCOOH
Thus, the alkene is (CH3)2C=CHCH2CH2CH=CH2
Option B is the correct one.
Note:
Ozonolysis means the addition of ozone molecules to alkenes. Ozonide will be formed in the reaction. Later the oxidative work up means the oxidation takes place. But only aldehydes convert into carboxylic acids. The ketones will not convert into carboxylic acids is an important point.
