Question
Question: A car moves on a circular path of radius \(5 m\). At one instant the speed of the car is \(5m/s\) an...
A car moves on a circular path of radius 5m. At one instant the speed of the car is 5m/s and it is decreasing at a rate of 5m/s2. The angle between the acceleration vector and the velocity vector at this instant is:
A) 3π
B) 4π
C) 32π
D) 43π
Solution
The rate of change of the position of the object is represented by a velocity vector. The magnitude represents the speed of the object and the direction gives its direction. According to the vector addition, vectors can either be added or subtracted as per the situation.
Complete step by step solution:
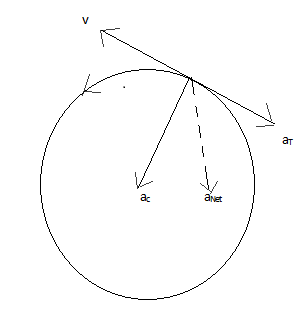
Given data:
The Radius of the circular path, r = 5m
The speed of the car,v = 5m/s
The tangential acceleration, aT=5m/s2
The angle between the acceleration vector and the velocity vector =?
The centripetal acceleration is given by the formula, ac=rv2
Substituting the values of r and v, we get
ac=552=525=5m/s2
⇒ac=5m/s2
Thus the net acceleration will be equal to 252+52at an angle of 4πto the tangential acceleration.
∴ The angle =π−4π=43π
Hence the angle between the acceleration vector and the velocity vector is 43π.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: 1. Whenever there is a change in the velocity of the body, then we can say that the body is accelerating. The rate at which the body changes its velocity is called acceleration. It is a vector quantity and thus has both magnitude and direction. The acceleration vector does not change with time and it is constant.
2. The velocity vector and the acceleration vector are always perpendicular to each other in case of uniform circular motion.
3. In the coordinate system, when the object is moving in the positive direction, we can say that it is a positive vector, and when it is moving in the opposite direction, we can say that it is a negative vector.
