Question
Question: A car moves at constant speed on a road as shown in the figure. The normal force by the road on the ...
A car moves at constant speed on a road as shown in the figure. The normal force by the road on the car is when it is at point A and B respectively. Information to decide the relation of
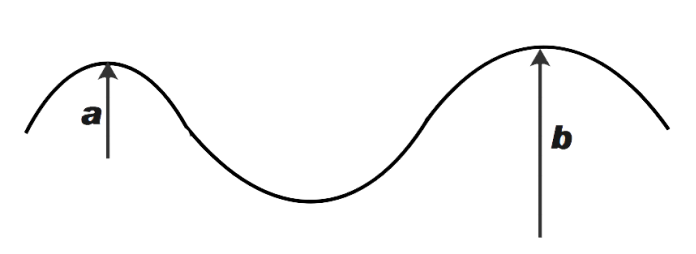
A. NA=NB
B. NA>NB
C. NA<NB
D. insufficient
Solution
In this question we are being asked to find the relation between NA and NB. From the figure, it is clear that radius of curve a is less than radius of curve b. NA and NB are the normal forces at point A and B. We know that, formula for calculating the normal force on a curved road, states the relation between velocity and the radius of the curve. The velocity is not given as constant at both points.
Formula used:
N=mg−rmv2
Where,
Mg is the weight of the car
V is the velocity
And r is the radius of the curve
Complete step-by-step answer:
From the figure, we can say that radius of curve a say rAis less than radius of curve B say rB. We know that, weight of the car will remain constant at all times. The velocity at point a and point b is given as constant
Now,
We know from formula,
N=mg−rmv2
We can say that the normal force N is directly proportional to square of velocity v and inversely proportional to the radius of curve r.
Now, the normal force at point a say NA can be given as
NA=mg−rAmvA2 ……………. (1)
Similarly, the normal force at point b sayNB can be given as
NB=mg−rBmvB2 ………………………….. (2)
Now let us assume that NA = NB
Therefore, from (1) and (2)
We can say that,
mg−rAmvA2=mg−rBmvB2
On solving we get,
rAvA2=rBvB2
But we know that velocity is constant
Therefore,
rA1=rB1
But from the diagram given, we know that rA < rB
Also, we know that the normal force N is inversely proportional to radius r
Therefore, we can say that our assumption is wrong.
Since rA < rB, we can now say that
NA>NB, since the normal force is inversely proportional to r
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The normal force is said to be the support force. For a normal force to act on a body the body must be in contact or lying on the surface. The normal force for static objects on a horizontal plane is usually taken as the weight of the object i.e. mg. In such cases normal force is counteracting the weight of the object.
