Question
Question: A capacitor of capacitance \(1\mu F\) withstands the maximum voltage of 6 kV, while another capacito...
A capacitor of capacitance 1μF withstands the maximum voltage of 6 kV, while another capacitor of capacitance 2μF withstands the maximum voltage of 4 kV. If they are connected in series, the combination can withstand a maximum voltage of
A) 3 kV
B) 6 kV
C) 10 kV
D) 9 kV
Solution
The charge present on the respective capacitors can be calculated minimum out of which will be the maximum charge (as more charge than that will break the circuit). The maximum voltage can be calculated using this maximum charge and respective capacitances.
Formula to be used:
C=Vq where,
C = Capacitance
q = Charge
V = Voltage
For conversions:
1μF=10−6F
1 kV→103V
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
Capacitance capacitor of 1 (C1)= 1μF→10−6F
Maximum voltage capacitor 1 can withstand (V1) = 6 kV→6×103V
Capacitance capacitor of 2 (C2) = 2μF→2×10−6F
Maximum voltage capacitor 2 can withstand (V2) = 4 kV→4×103V
As, capacitance is defined as charge upon volume:
C=Vq ___________ (1)
q=CV
The maximum value charge each capacitor can have can be given as:
For capacitor 1:
q1=C1V1
Substituting the values, we get:
q1=10−6×6×103 q1=6×10−3C
For capacitor 2:
q2=C2V2
Substituting the values, we get:
q1=2×10−6×4×103 q1=8×10−3C
When we connect them in series, the circuit can be given as:
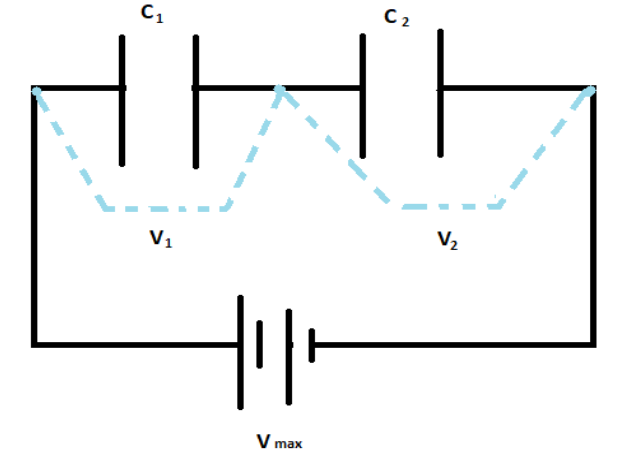
V1 and V2 are effective voltages across the capacitors and Vmax is the required maximum voltage which can be given as:
Vmax=V1+V2 __________ (2)
Now, the maximum allowed on both the will be the minimum out of two because if the charge is more than that the circuit will break.
qmax=q1=q2 qmax=6×10−3C
Using (1):
C=Vq
V=Cq
From (2):
Vmax=V1+V2
Vmax=C1q1+C2q2
Substituting the given values, we get:
Vmax=10−66×10−3+2×10−66×10−3
Vmax=9×103
Vmax=9kV
Therefore, if the given capacitors are connected in series, the combination can withstand a maximum voltage of 9 kV and hence the correct option D).
Note: SI units of various quantities are:
Capacitance (C) = Faraday (F)
Voltage (V) = Volts (V)
Charge (q) = Coulombs (C)
Capacitors are used to store energy as electric charge and hence are used for charging purposes.
