Question
Question: A body weighing \( 0.4kg \) is whirled in a vertical circle with a string making 2 revolutions per s...
A body weighing 0.4kg is whirled in a vertical circle with a string making 2 revolutions per second. If the radius of the circle is 1.2m . Find the tension (a) at the top of the circle, (b) at the bottom of the circle. Given; g=10ms−2 and π=3.14
Solution
Hint In a vertical circle, the weight of the body affects the tension on the string. At the top the weight provides some of the centripetal force required for circular motion. At the bottom, it increases the centripetal force required. So we need to set the equation for the body and from there we can calculate the tension in the string.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formula;
⇒FNET=ma , where FNET is the net force acting on a body, m is the mass of the body, and a is the acceleration attained by the body.
⇒ac=mω2r , where ac is the centripetal acceleration of a body moving in a circular motion, ω is the magnitude of the angular velocity of the body and r is the radius of the circle.
Complete step by step answer
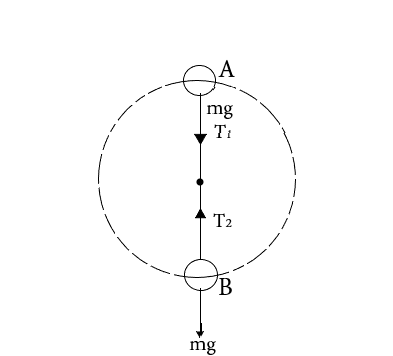
During a vertical swirl, the weight of the object plays an important role in the determination of the tension on the string. Depending on the immediate location of the body, it can either add to tension or relieve it. To calculate the tension, we analyse the motion using Newton’s second law of motion. Thus,
⇒FNET=ma where FNET is the net force acting on a body, m is the mass of the body, and a is the acceleration attained by the body.
A) At point A on the vertical swirl (top if the circle):
⇒T1+mg=mac where T is the tension, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and ac is the centripetal acceleration directed inward towards the centre of the circle.
Centripetal acceleration in general can be given as
⇒ac=mω2r where ω is the magnitude of the angular velocity of the body and r is the radius of the circle.
According to the question, ω=2rev/s , converting to SI unit, we multiply by 2π (since 1 rev subtends 2π radians), hence
⇒ω=12.56rad/s or ω=12.56s−1 .
Hence, we calculate mac from all known variables
⇒mac=0.4(12.56)2×1.2=75.72N
Hence,
⇒T1+0.4(10)=75.72
Thus,
⇒T1=75.72−4
⇒T1=71.72N
B) For point B (bottom of circle)
⇒T2−mg=mac , (since tension and weight point in opposite direction)
Similarly,
⇒T2−0.4(10)=75.72
Thus,
⇒T2=75.72+4
⇒T2=79.72N .
Note
Alternatively we can calculate centripetal force from
⇒mac=rmv2 where v is the magnitude of the linear speed.
We calculate v from v=ωr . Thus,
⇒v=12.56(1.2)=15.072m/s
⇒mac=1.20.4(15.072)2=75.72 which is identical to the above.
