Question
Question: A body covers first \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)part of its journey with a velocity of \(2m/s\), next \(\dfrac{1...
A body covers first 31part of its journey with a velocity of 2m/s, next 31 part with a velocity of 3m/sand the rest of the velocity is 6m/s. The average velocity of the body will be,
a. 3m/s
b. 311m/s
c. 38m/s
d. 34m/s
Solution
We can solve the given equation by finding the value of the average velocity of the body. We know the formula for the velocity that is displacement by time.
Formula used:
Velocity=timedisplacement
Complete step by step answer:
We can consider the given values in the question. In the question it is given that the body covers first 31 part of its journey with a velocity of 2m/s, next 31 part with a velocity of 3m/s and the rest of the velocity is 6m/s.
Now we can draw a diagram with the given data.
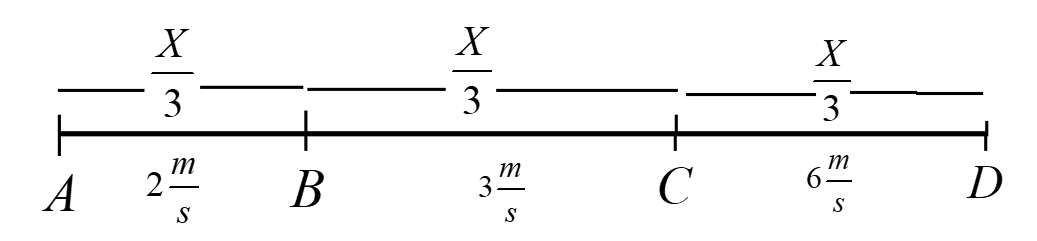
In the given diagram the values are mentioned. The velocities are 2m/s, 3m/s,6m/s. With the displacement of 3X.
We need to calculate the value of the average velocity. Velocity in physics is defined as the rate of change of the position of the object that is displaced with respect to the time of the reference frame. We need both the values of magnitude and the speed explains the velocity. In short, the velocity is the vector quantity. The meter per second (m/s) is the S.I unit for the velocity. The velocity is the function of the displacement. The change in the velocity indicates that there is an acceleration acting on the object in a direction. The instantaneous velocity is the velocity of the time in a given moment and the average velocity can be calculated by dividing the total displacement and total time.
Now let us solve the given problem. We know the formula for the velocity. That is,
Velocity=timedisplacement
To calculate the average velocity, we need to divide the total displacement and the total time taken. That is,
Vaverage=T.TT.D
Where, Vaverage is the average velocity, T.D is the total displacement and T.T is the total time taken.
Time taken can be calculated as displacement by velocity. That is,
⇒t1=23xX⇒t1=6xX
⇒t2=33xX⇒t2=9xX
⇒t3=63xX⇒t3=18xX
By substituting the value of time in the equation we get,
⇒Vaverage=T.TT.D
⇒Vaverage=6x+9x+18xX
On cancelling the x terms we get,
⇒Vaverage=61+91+1811
Taking L.C.M we get,
⇒Vaverage=3+2+118
∴Vaverage=3m/s
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The difference between the speed and the velocity must be known. Speed and velocity can be a little confusing, but note that speed gives the idea about how the object is moving. Whereas the velocity tells about the direction and the speed of the object.
