Question
Question: A block of mass 5 kg is initially at rest on a rough horizontal surface. A force of 45 N acts on it ...
A block of mass 5 kg is initially at rest on a rough horizontal surface. A force of 45 N acts on it in a horizontal direction and pushes it over a distance of 2 m. The force of friction acting on the block is 25 N. The final kinetic energy of the block is
A. 40 J
B. 90 J
C. 50 J
D. 140 J
Solution
Frictional force opposes the applied force and creates a hindrance in motion. If we are applying some force to push the block forward then the contribution from friction has to be subtracted as it will create retardation.
Formula used:
Force of friction when subtracted from the applied force will give the net force forward that acts on the body.
Fapplied−Ffriction=Fnet.
As kinetic energy is the work done so:
K.E. = Work = Force × displacement.
Complete answer:
We are given the magnitude of applied force as 45 N and the magnitude of frictional force as 20 N.
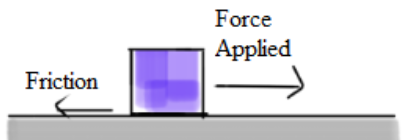
If we suppose that the applied force is acting along +x direction, then the frictional force is opposite in this motion and acting along -x direction. Therefore the net force in +x direction (or forward direction) that will be responsible for the motion of the block is:
Fnet= (45-25) N = 20 N.
Under the influence of this net force, the block moves by a distance of 2 meters. Therefore the work done by this force on the block is given as:
Work = Force × displacement;
W = 20 N × 2 m.
W = 40 Nm = 40 J.
As this work done is nothing but the kinetic energy of the block.
So the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
Another way of doing this is by using the kinetic energy formula, (1/2)mv2. As we found out the net force and we are already given the mass of the block, we would have found the acceleration by dividing the net force by the given mass. Then, using a third law of motion we could have found out the velocity (with u = 0). And substituting velocity in the K.E. formula would have provided us the same answer.
