Question
Question: A battery of emf \(2\) voltage and internal resistance \(0.1\) ohm is being charged with a current o...
A battery of emf 2 voltage and internal resistance 0.1 ohm is being charged with a current of 5 amperes. The potential difference between the two terminals of the batteries is
(A)2V(B)0.5V(C)1.5V(D)2.5V
Solution
Potential difference is defined as the work done from moving a unit positive test charge from one point to another. In order to find the potential difference between the two terminals of the battery, completely understand the electrical system, the direction of flow of charge, and then apply the sign convention accordingly to the mathematical expression for potential difference.
Formula used:
V=E+i×Rint
Complete answer:
Given in question is the following electrical circuit:
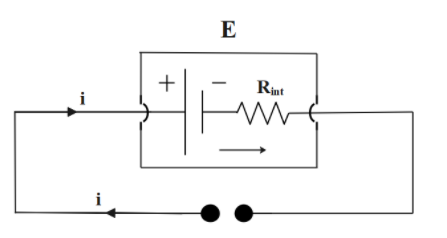
The values of the system variables are given as:
E=2VRint=0.1Ωi;=5amp
When a cell is being charged the potential drop across it is given by the following relationship:
V=E+i×Rint
Hence,
\eqalign{
& V = 2 + 0.1 \times 5\;volts \cr
& \therefore V = 2.5V \cr}
So, the correct option for this is option (D).
Additional Information:
A part of the battery with more than electrons, and another spare a scarcity of electrons. The excess electrons want to travel to the opposite side (because like charges repel), which generates a voltage. If you complete the circuit and let the electrons attend the opposite side, the difference in the number of electrons will go down and therefore the remaining ones will want to maneuver to the opposite side less (lower voltage). Eventually, the electrons are balanced, and therefore the battery is dead because it does not feature an electric potential.
Note:
Measure the quantity of resistance within the circuit. Resistance comes from a resistor, a tool within the circuit, or just the quantity of resistance from the conductor (wire) within the circuit. Multiply the quantity of the present by the quantity of resistance within the circuit. The electric potential or potential difference during a circuit is what causes current to flow through the circuit. The larger the electric potential, the faster the present will flow, and therefore the higher the present. The electric potential is the measure of the difference in voltage between two distinct points during a loop.
