Question
Question: A barometer is faulty. When the true barometer readings are 73 and 75 cm of Hg, the faulty barometer...
A barometer is faulty. When the true barometer readings are 73 and 75 cm of Hg, the faulty barometer reads 69 cm and 70 cm respectively. What is the total length of the barometer tube?
Solution
In an actual barometer the pressure above the mercury level in the tube is zero. In a faulty barometer, the air is unable to escape completely and creates some additional pressure. In any measurement, the same amount of air is struck i.e., the number of molecules does not change.
Formula used:
To find out the length of the tube, we can use the relation:
(l−l1)e1=(l−l2)e2
Where we have e1 as an error in the first reading corresponding to difference between actual length and faulty length l1 so is for the second reading error e2 .
Complete step-by-step answer:
A barometer is a device that measures pressure by indicating a specific rise in its Mercury level corresponding to that pressure.
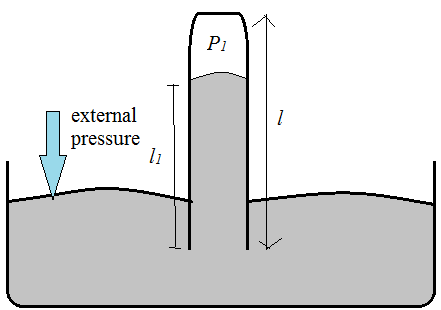
When the tube has a length l (which is for the faulty case), there is an additional pressure due to air which adds to the mercury pressure. Therefore, we get an expression: P1+dl1g=dh1g ;
where h1 is the height of actual mercury for the same external pressure. The RHS corresponds to external pressure on the mercury and LHS corresponds to the situation inside the tube.
We can get the air pressure as: P1=dg(h1−l1)
Similarly, the pressure during second reading will be: P2=dg(h2−l2)
Now, we are familiar with another expression for gas pressure: P1V1=nRT=P2V2
Where we have also equated the pressure when the level in the tube becomes l2. We can show that:
V1=A×(l−l1) V2=A×(l−l2) when the area of the cross section of the tube will be A.
For the sake of simplicity, let us first write down, h1−l1=(73−69)cm= 4cm. And h2−l2=(75−70)cm= 5cm. (From the given values).
Now substituting the values into P1V1=P2V2 will give us: dg(4)×A(l−69)=dg(5)×A(l−70) 4l−4×69=5l−5×70.
Which upon simplification gives us the value; l = 74 cm;
which is the required total length of the faulty barometer tube.
Note: As the length of the faulty barometer is different from actual barometer tube, vacuum is not formed above the mercury level in case of faulty barometer. The pressure outside will be correctly measured by the actual barometer (it will be hdg) so we keep that as the external pressure in the formula. Since the pressure is the same everywhere, so the internal pressure due to mercury level + air pressure was equated with the correct external pressure.
