Question
Question: A balloon is observed simultaneously from three points \(A,B,C\) on the straight road directly under...
A balloon is observed simultaneously from three points A,B,C on the straight road directly under it. The angular elevation at B is twice that of A and the angular elevation at C is thrice that of A. If the distance between A and B is 200m and the distance between B and C is 100m, find the height of the balloon.
A. 503m
B. 50m
C. 1503 m
D, 1003m
Solution
In this question, we will firstly draw the figure according to the given information. We will locate the points A,B,C on the straight line and then try to find out the relations in the angle of elevation with respect to the three given points. We will use the trigonometric functions and then use the distance between the points, we will easily get the height of the balloon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
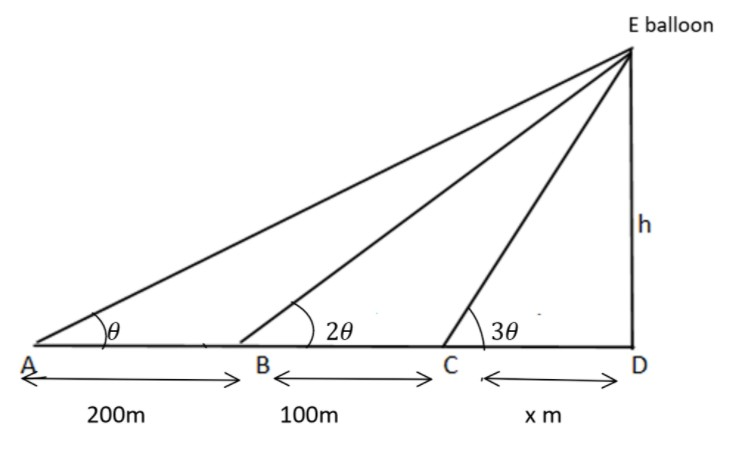
Given A,B,C are the three points on the straight road and a balloon is observed from the three points. The angular elevation at B is twice that of A. Let the angle of elevation at Ais θ, then the angle of elevation at B is 2θ. Also the angular elevation at C is thrice that of A, so it will be 3θ.
Hence the angle of elevation at A,B,C are θ,2θ,3θ.
So, the above is the diagram for this question.
From given information we distance between A and B is 200m, so
AB=200m −−−−−(1)
Similarly, it is given that distance between B and C is 100m, so
BC=100m −−−−−(2)
Let distance between C and D is x, that is,
CD=x −−−−−(3)
Let height of the balloon be ED=h−−−−−(4)
Now according to the question, we have to find the height of the balloon that is, h
Now, it is clear from the above figure that height of the balloon is perpendicular for the right-angled triangles EDC, EDB and EDA. Using trigonometric formulas for these right-angled triangles we will get some equations involving h and by solving these equations we can easily get the value of h.
Now let’s work according to above procedure-
And firstly, taking triangle EDC,
We can clearly see from the figure that EDC is a right-angled triangle.
We know tanθ=baseprependicular, now using it for angle 3θ, we get,
So, tan3θ=baseperpendicular=CDED
Using (3) and (4) and substituting values of ED and CD, we get,
tan3θ=xh
Now simplifying it further we get
x=tan3θh
Using cot3θ=tan3θ1, we get
x=hcot3θ−−−−−−(5)
Secondly, consider the right-angled triangle EDB and again using, tanθ=baseperpendicular for angle 2θ, we get
tan2θ=BDED
Now using (2) to substitute value of ED and using figure we can say BD=BD+CD, we get,
tan2θ=BC+CDh BC+CD=tan2θh
Now we know that, tanθ1=cotθ, we get,
BC+CD=hcot2θ
Using (2) and (3) and substituting BC=100m and CD=x, we get,
100+x=hcot2θ−−−−(6)
Now taking the triangle EDA right-angled at D,
Again using, tanθ=baseperpendicular
tanθ=ADED
Now using figure, we can directly see AD=AB+BC+CD and using (2) to substitute value of ED, we get
tanθ=AB+BC+CDh
Now using (1), (2) and (3) to substitute values of AB, BC and CD, we get
tanθ=200+100+xh=300+xh ⇒tanθ=300+xh
Now further solving it, we get
300+x=tanθh
Now again, tanθ1=cotθ, we get,
300+x=hcotθ−−−−−(7)
Now subtracting equation (5) from (6), we get
100+x−x=hcot2θ−hcot3θ
100=h(cot2θ−cot3θ)−−−−−(8)
Now subtracting equation (6) from (7), we get
200=h(cotθ−cot2θ)−−−−−(9)
Now dividing equation (8) by (9),
200100=h(cotθ−cot2θ)h(cot2θ−cot3θ)
Now h is cancelled from numerator and denominator, we get
21=(cotθ−cot2θ)(cot2θ−cot3θ)
Now using, cotθ=sinθcosθ for cotθ,cot2θ and cot3θ, we get,
21=sinθcosθ−sin3θcos3θsin2θcos2θ−sin3θcos3θ
\dfrac{{\cos \theta }}{{\sin \theta }} - \dfrac{{\cos 3\theta }}{{\sin 3\theta }} = 2\left\\{ {\dfrac{{\cos 2\theta }}{{\sin 2\theta }} - \dfrac{{\cos 3\theta }}{{\sin 3\theta }}} \right\\}
Now taking L.C.M., we get,
sinθsin2θsin2θcosθ−sinθcos2θ=sin2θsin3θ2(sin3θcos2θ−sin2θcos3θ)
Now cancelling sin2θ1 from both sides, we get
sinθsin2θcosθ−sinθcos2θ=sin3θ2(sin3θcos2θ−sin2θcos3θ)
Now using, sinAcosB−sinBcosA=sin(A−B), where for L.H.S A=2θ and B=θ and for R.H.S A=3θ and B=2θ, we get,
sinθsin(2θ−θ)=sin3θ2sin(3θ−2θ)
sinθsinθ=sin3θ2sinθ
1=sin3θ2sinθ
Now solving further, we get,
sinθsin3θ=2
Now using formula,
sin3θ=3sinθ−4sin3θ and substituting value of sin3θ, we get
sinθ3sinθ−4sin3θ=2
Now taking sinθ common from numerator, we get,
sinθsinθ(3−4sin2θ)=2
Now cancelling sin3θ from L.H.S, we get
3−4sin2θ=2
1−4sin2θ=0
Now further solving we get
sin2θ=41
⇒θ=6π
Substituting θ=6π in equation (9), 200=h(cotθ−cot2θ) to get value of h
So,
200=h(cot6π−cot3π)
Now substituting cot6π=3 and cot3π=31, we get,
200=h(3−31)
By solving this above equation, we get,
(3−31)200=h
Now solving it further, we get,
⇒h=(33−1)200=22003 ⇒h=1003
Hence h=1003m
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: In the above problem we use the trigonometric function which should involve perpendicular and the base. So we use tanθ. And here we need to find the height and the base from a given right angled triangle. And we should try to understand which trigonometric function we should apply in order to get the desired result.
