Question
Question: A ball thrown by a boy is caught by another after 2 sec some distance away in the same level. If the...
A ball thrown by a boy is caught by another after 2 sec some distance away in the same level. If the angle of projection is 30∘, the velocity of the projection is
A. 18.0
B. 19.6
C. 20.0
D. 18.6
Solution
Recall the expression for the time of flight of the projectile. Rearrange the expression for the initial velocity. Substituting the values of the angle of projection, time of flight, and acceleration due to gravity in this formula, you will get the initial velocity.
Formula used:
Time of flight, T=g2usinθ
Here, u is the initial velocity of the ball and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the time of flight of the ball is T=2sec and the angle of projection is θ=30∘.We have the expression for the time of flight for the projectile is,
T=g2usinθ
Here, u is the initial velocity of the ball and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Rearranging the above equation for u, we get,
u=T×2sinθg
Substituting T=2sec, θ=30∘ and g=9.8m/s2 in the above equation, we get,
u=2×2sin(30)9.8
⇒u=2×2(21)9.8
∴u=19.6m/s
Therefore, the initial velocity of the ball is 19.6 m/s.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Additional information:
We can derive the formula for time of flight using the kinematic equation.
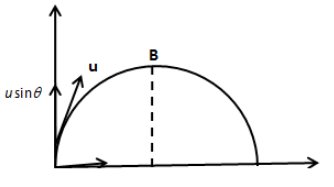
At point B, the velocity of the ball becomes zero. Using the kinematic equation in the vertical direction, we get,
v=usinθ−gt
⇒0=usinθ−gt
⇒usinθ=gt
⇒t=gusinθ
Since the time of ascend is equal to the time of descent. Therefore, the total time required to hit the ground is,
T=2t=g2usinθ
Note: Students don’t need to derive the formula for the time of flight and can use the formula that mentioned in the above solution. Since the acceleration due to gravity is constant, the time of flight depends only on the initial velocity and the angel of projection. The time of flight would be different if another boy is not at the same level as the first boy.
