Question
Question: A 6V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length 1m. The ...
A 6V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length 1m. The positive terminal of another battery of emf 4V and internal resistance 1Ω is joined to the point A as shown in the figure. The ammeter shows zero deflection when the jockey touches the wire at the point C. The length AC is equal to
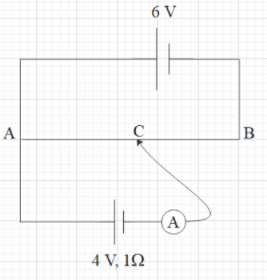
Solution
When the ammeter shows zero reading, the potential difference between AC is equal to the emf of the battery of 4V. The potential difference across the wire AB is 6V. So find the potential difference per unit length of the wire. Then find the length for which the potential difference is equal to 4V.
Formula used:
l=VEL
Complete answer:
Since, the battery of 6V has negligible internal resistance, the potential difference across the uniform wire AB is equal to the emf of this battery, i.e. 6V.
Due to this potential, a current will flow in the circuit.
Now another battery of emf 4V and internal resistance 1Ω is connected as shown. Until there is some potential difference across the ammeter, a current will flow through the ammeter. Hence, the ammeter will show some reading.
It is given that that ammeter shows zero reading when the jockey touches the wire AB at point C. This means that the potential difference across the ammeter is zero.
This also means that the potential of the negative terminal of the 4V battery is equal to the potential at point C.
As we can see that the point A and the positive terminal of this battery are at the same potential.
Therefore, we can say that the potential difference between AC is equal to 4V.
The length of AC be l.
The potential difference across AB is 6V and the length of AB is 1m. Therefore, the potential difference per unit length of this wire is 16=6Vm−1.
This means that the potential difference for every one meter is 6V. Therefore, the potential difference for a length l will be V=6l.
And we found that the potential difference for length l is 4V.
Therefore, 4 = 6l.
l=64=0.66m.
Hence, the length AC is equal to 0.66m.
Note:
The given circuit diagram is of a potentiometer. A potentiometer is used to measure the emf of an unknown cell. The length AC, when the ammeter shows zero reading is called as balancing length l and is given by l=VEL.
Here, E is the emf of the unknown cell (the one with less emf), V is the potential difference across the wire AB and L is the length of AB.
⇒l=VEL=64(1)=0.66m
