Question
Question: A 2144kg freight car rolls along rails with negligible friction. The car is brought to rest by a com...
A 2144kg freight car rolls along rails with negligible friction. The car is brought to rest by a combination of two coiled springs as illustrated in Fig. 1. Both springs are described by Hooke's law with k1=1600 Nm−1 and k2=3400 Nm−1. After the first spring compresses a distance of 30.0 cm, the second spring acts with the first to increase the force as additional compression occurs as shown in the graph in Fig. 2. The car comes to rest 50.0 cm after first contracting the two-spring system. Find the car's initial speed (in ×10−1 ms−1).
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 8
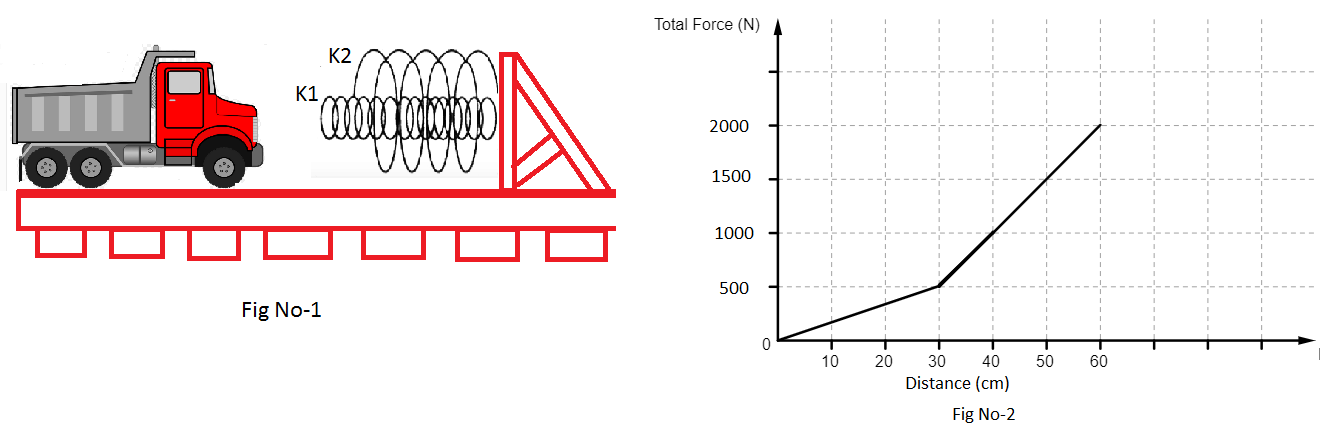
Solution
Start with assuming the initial speed of car to be some variable. Apply the formula of kinetic energy i.e. 21mv2 to determine the change in its kinetic energy. Further, use the formula of work done by a spring i.e. −21kx2 to determine the total work done by the spring on the car. Then apply a work-energy theorem to get the answer. According to this theorem, the total work done by the external forces on a particle is equal to change in its kinetic energy.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, at first, only the first spring is compressed up to the distance of 30 cm or 0.3 m (as 100 cm = 1 m) and then it compresses another distance of 20 cm or 0.2 m along with the second spring to complete the total 50 cm or 0.5 m of compression. But the second spring is compressed only up to 20 cm or 0.2 m i.e. for the later part.
Let x1 and x2 be the final compression in the first and second springs respectively. Then as per the above discussion, we have:
⇒x1=50 cm=0.5 m and x2=20 cm=0.2 m
We know that the work done by a compressed spring having k as its spring constant and x as the length of compression, is given as:
⇒W=−21kx2
The spring constants of springs are also given in the question. k1=1600 Nm−1 and k2=3400 Nm−1 are the spring constants of first and second springs respectively.
Applying the formula, total work done on the car by the first spring is:
⇒W1=−21k1x12=−21×1600×0.52 ⇒W1=−200J
Similarly, the work done on the car by the second spring is:
⇒W2=−21k2x22=−21×3400×0.22 ⇒W2=−68J
So, the total work done on the car by both the springs is:
⇒W=W1+W2=−200J−68J ⇒W=−268J .....(1)
According to the work-energy theorem, we know that the total work done on a body by the external forces must be equal to change in its kinetic energy. Thus the total work done by the springs on the car must be equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
Let the initial velocity of the car is v1. From the question, the car is coming to rest finally. So its final velocity is zero i.e. v2=0
We know that the kinetic energy of a particle moving at a speed of v is given as 21mv2, where m is its mass. So the change in kinetic energy of the car is:
⇒ΔK=21mv22−21mv12
Putting v2=0, we’ll get:
⇒ΔK=21m×02−21mv12 ⇒ΔK=−21mv12
From the work-energy theorem as discussed above, the total work done by the springs on the car must be equal to the change in its kinetic energy. So, we have:
⇒ΔK=W
Putting the values of ΔK from above and of W from first equation, we’ll get:
⇒−21mv12=−268J
Mass of car is given in the question as 2144 kg. Putting this, we’ll get:
⇒21×2144×v12=268J ⇒v12=2144268×2=0.25 ⇒v1=0.5 ms−1
Therefore the initial velocity of car is 0.5 ms−1=5×10−1 ms−1.
Hence, option (A) is the correct option.
Note: We cannot apply the energy-conservation theorem for this problem. Energy-conservation theorem is applied only when no external force is acting on the system. If we take a car as a system, the force applied by springs on it is an external force. While if we take both car and springs as a system then the force applied by the support at the back of the spring (as shown in the figure) to keep it stationary, is an external force. But spring and truck together can be taken as a system as on them the net external force is zero.
