Question
Question: 2-pentanone and 3-pentanone are: A) Chain isomers B) Tautomers C) Metamers D) Positional iso...
2-pentanone and 3-pentanone are:
A) Chain isomers
B) Tautomers
C) Metamers
D) Positional isomers
Solution
The answer here is based on the basic concept of organic chemistry which deals with the stereochemistry part that tells us about the arrangement of atoms in a molecule in the three dimensional geometry.
Complete Solution :
We have studied the concepts of organic chemistry about the chapters that deal with stereochemistry and this concept tells us about the arrangement of atoms in a molecule in space.
Now, let us see the meaning of each term given in the option which will later help us to conclude the right answer.
- Stereochemistry is the part of organic chemistry which deals with the study of how the molecule is affected by the arrangement of their atoms in the space.
- This stereochemistry is also known as three dimensional or 3D chemistry as the word ‘stereo’ itself has a meaning ‘three’ and this is based upon our imagination of the atoms in the space.
- Chemists use this part of chemistry to study the relationship between the molecules that are made up of the same atoms.
- In option A) Chain isomers are those compounds that are having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of the carbon skeleton.
- In option B) Tautomers are the structural isomers that can readily interconvert and basic example is that carbonyl group converts into alcohol group with the addition of double bond to its respective carbon atom.
- In option C) Metamers are those in which the carbon chain varies but the functional group remains in the same position.
- In option D) Position isomer simply means the constitutional isomers that have the same carbon skeleton and also same functional group but differ in the location of the functional group on or in the carbon chain.
- Now, based on all these definitions, we can say that the given compound is the positional isomers because the position of the keto group changes.
Therefore, this can be shown in the structure as given below:
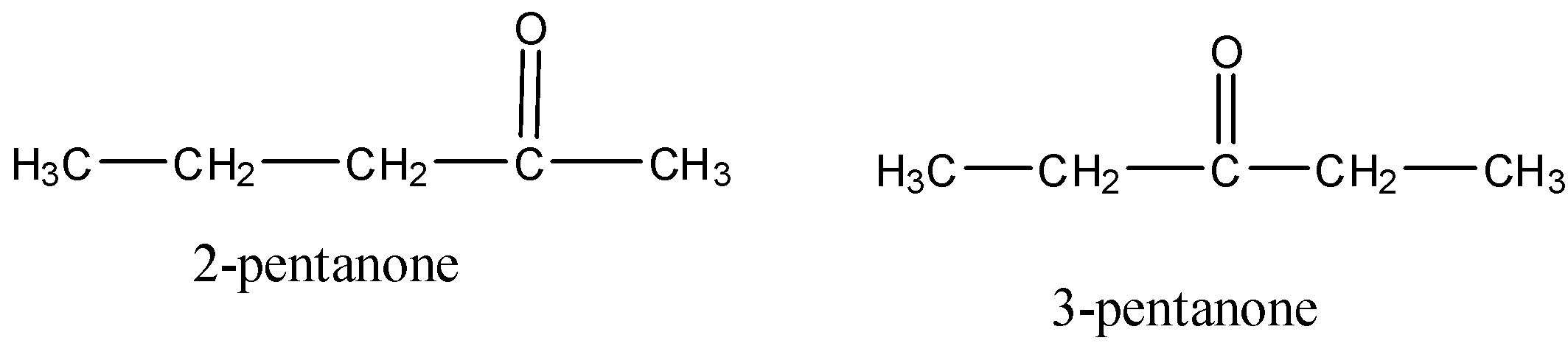
In the above structures we can see that the carbonyl group changes from its actual position to the other.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that positional isomers and metamers are different although it sounds same and main difference is that positional isomers is just a change in the position of functional group and no change in the carbon chain whereas metamers are those in which functional group is fixed but alkyl group changes its position.
