Question
Question: 2-hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment with (A)\(Pt/H_2\) (B)Li/\({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}...
2-hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment with
(A)Pt/H2
(B)Li/NH3
(C)Pd/BaSO4
(D)LiAlH4
Solution
We know that a trans isomer is a isomer in which functional groups are present at the opposite side of the carbon chain and a cis isomer is a isomer in which functional groups are present at the same direction of carbon chain.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, 2-hexyne undergoes reduction to form trans-2-hexene.
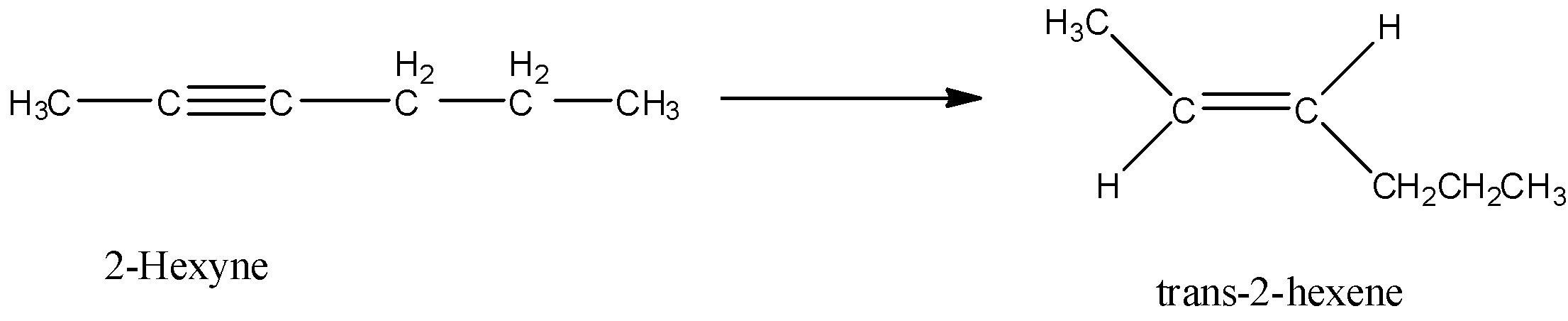
Let’s discuss the given options one by one.
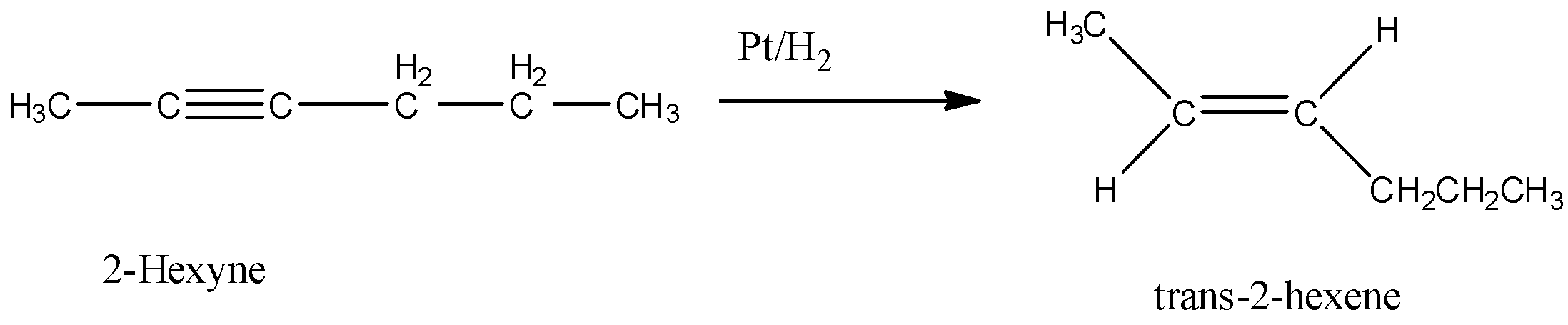
Option A is Pt/H2. Hydrogenation in presence of platinum reduces an alkyne to alkene. In this reduction reaction, hydrogen atoms are added by the trans addition, that means, on the opposite side of the double bond. So, when 2-hexyne undergoes reaction with Pt/H2, trans-2-hexene is formed.
Option B is Li/NH3. Li/NH3 is also called a Lindlar catalyst. This catalyst is used to convert alkyne to alkene. But the hydrogen added is in cis manner. So, a cis-isomer obtained in the reaction. So, the formation of trans-2-hexene is not possible by the Lindlar catalyst.
Option C is Pd/BaSO4. Pd/BaSO4 is also a reducing agent. It reduces an alkyne to an alkene. The alkene formed is cis-isomer. So, the formation of trans-2-hexene is not possible by Pd/BaSO4.
Option D is LiAlH4(lithium aluminium hydride). Lithium aluminium hydride is a strong reducing agent. It can reduce polar multiple bonds such as C=O. It reduces aldehydes to primary alcohols, carboxylic acids and esters to primary alcohols. The reduction of isolated non-polar multiple bonds cannot be possible by LiAlH4. The reduction of alkynes by LiAlH4 is possible if an alcohol group is present nearby. So, the formation of trans-2-hexene is not possible by LiAlH4.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
It is to be noted that oxidizing agents are those chemical species that cause oxidation such as oxidation of alcohol to aldehyde, oxidation of aldehyde to carboxylic acid. Some common oxidizing agents are hydrogen peroxide, oxygen, chlorine etc.
