Question
Question: 2-hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment with: (A) \(Pt/{H_2}\) (B) \(Li/N{H_3}\) (C) \(Pd...
2-hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment with:
(A) Pt/H2
(B) Li/NH3
(C) Pd/BaSO4
(D) LiAlH4
Solution
2-hexyne has alkyne as a functional group. Trans isomer is an isomer in which the same groups are on the different side of the carbon-carbon double bond. Trans-2-hexene has an alkene functional group.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s write the structures of starting material and the product in order to have a better idea about the reagent.
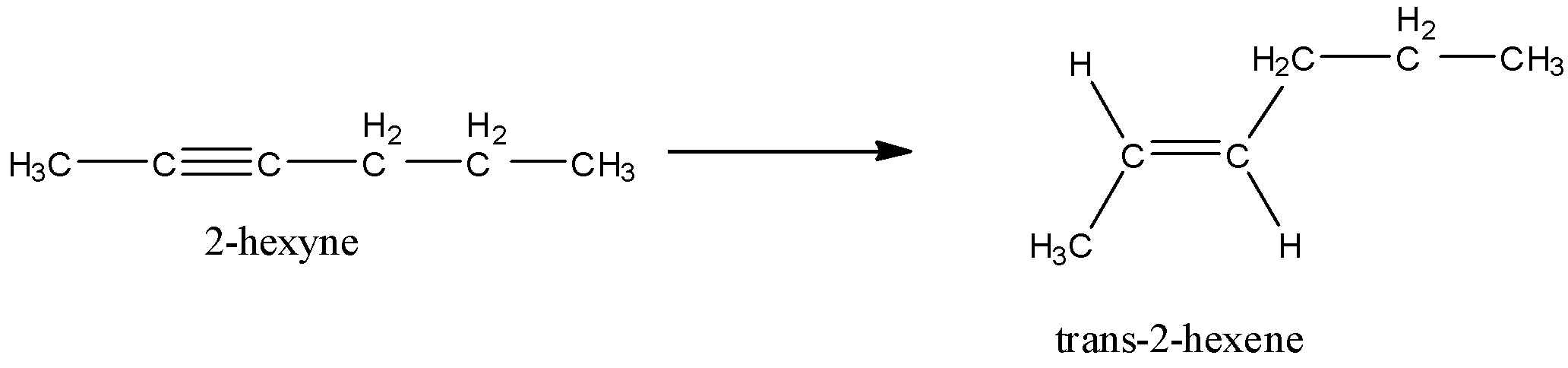
- Here, we can predict from the name 2-hexyne that this compound has an alkyne functional group. This functional group is at 2-position as given in the name.
- Now, the product is having an alkene functional group which can be predicted by –ene suffix. So, basically this reaction is a reduction reaction in which two hydrogen atoms are added across the carbon-carbon triple bond.
- But the main thing is stereochemistry here. The product is trans. That means the like groups are not on the same side of the C-C double bond.
- Hydrogen gas on Platinum metal can reduce the C-C triple bonds to C-C single bonds but we cannot separate the alkene product if it is used in equivalent amounts. So, it is not the correct answer.
- Li/NH3 is the reagent that selectively transforms alkyne into trans-alkene. This reaction occurs via a free-radical mechanism. Thus, it is a reduction reaction.
- Pd/BaSO4 is also called Lindlar’s catalyst and it reduces alkynes. The specialty of this reagent is that it gives cis-alkenes upon reduction from alkynes.
Thus, we can conclude that the correct answer is (B).
Note: Do not get confused between roles of Li/NH3 and Pd/BaSO4. Remember that Li/NH3 always gives trans alkenes as product while Pd/BaSO4 gives cis-alkenes exclusively.
