Question
Question: 1-Chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives: A..1-butene B. 1-butanol C.2-butene ...
1-Chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives:
A..1-butene
B. 1-butanol
C.2-butene
D. 2-butanol
Solution
Reagent can be a substance or mixture of compounds which are used in chemical analysis or reactions. When a reagent is added to a system it causes chemical reactions. For a particular reaction, a particular reagent gets consumed in the process of the chemical reaction. In this case, the reagent is an alcoholic potash. In presence of potash, an elimination reaction will occur.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, alcoholic potash is potassium hydroxide. When it reacts with 1 chlorobutane, the elimination reaction occurred.
Elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents get removed from the molecule in either two or one steps. Elimination reactions can occur from 1 and 2 positions, 1 and 3 positions, etc.
1,2 position elimination reaction is very common. When it is in one step then it is E2 elimination reaction. When it is in two steps then it is called E1 elimination reaction.
In elimination reaction, a strong base is required. Strong base abstract the proton at the beta position of the leaving group.
Now when 1-chlorobutane reacts with alcoholic potash the following reaction happens,
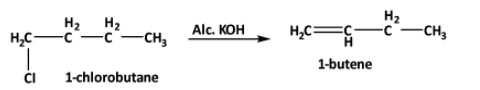
In this case, the E2elimination reaction happens.
So, the correct answer is, A.
Additional information:
To distinguish one from another use of reactions where a change of physical characteristics happens. For example, change of color of the solution, precipitation takes place, generation of effervescence, etc. let take the example of 1-butyne and 1-butene, which are shown below,

When both are treated with Ag(NH3)2+ which is called tollen’s reagent, the terminal alkyne reacts with tollen’s reagent and gives a white precipitate of acetylide. On the other hand, alkene does not react with it. These reactions are shown below,
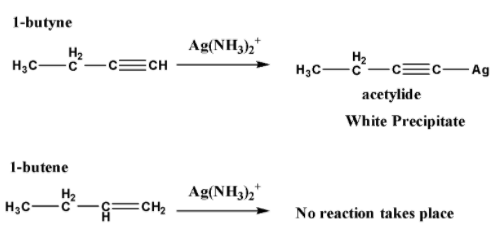
From this reaction, a change of physical characteristic happens which can be visualized to understand the difference between the 1-butyne and 1-butene.
Note:
Elimination reaction is a steric assistance reaction. With increasing the steric crowding of the substrate elimination reaction tendency increases and vice-versa. The E2 elimination reaction is a second-order reaction and E1 elimination reaction is a first-order reaction.
